Download PDF
Download page Monitor Azure Spring Cloud with Java Agent.
Monitor Azure Spring Cloud with Java Agent
Java Agent helps you monitor the workloads running in Azure Spring Cloud. To gain visibility into the topology of the application along with the data flows between the services, activate the Java Agent on services that make up your Azure Spring Cloud application.
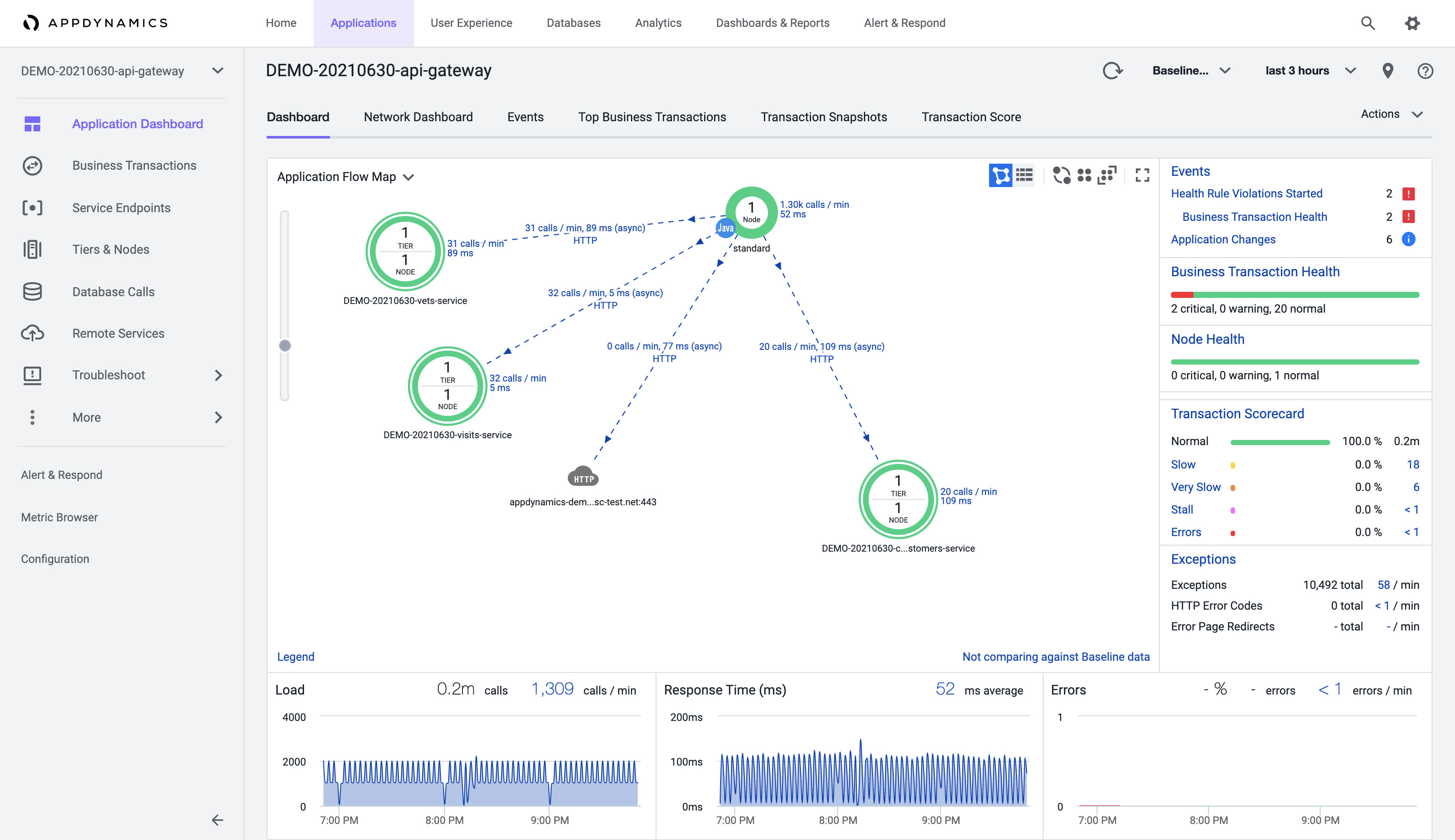
The Java Agent also provides root-cause analysis of slow or error transactions within the Azure Spring Cloud application.

The Java agent provides JVM memory usage of services within the Azure Spring Cloud application along with garbage collection information.
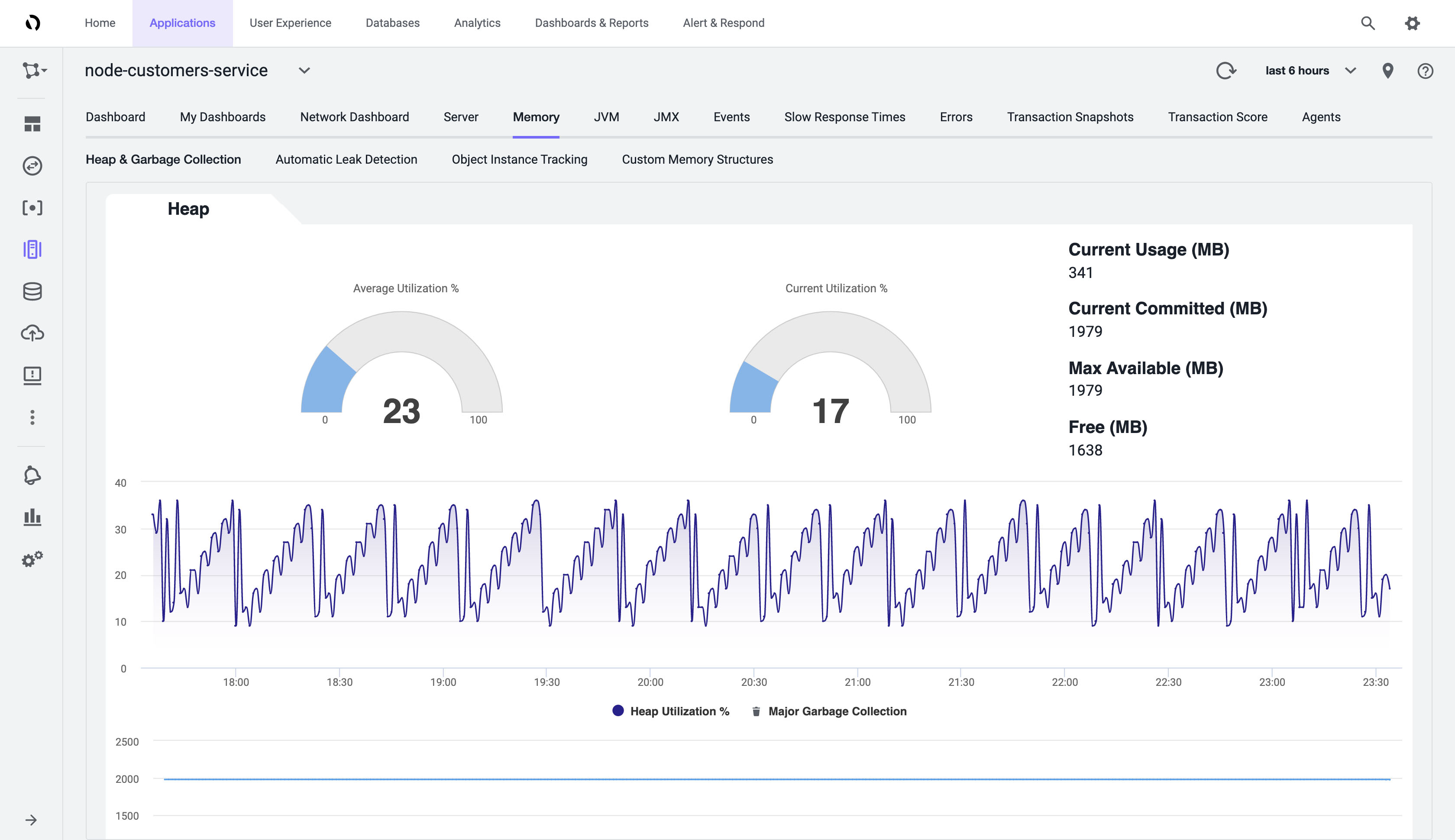
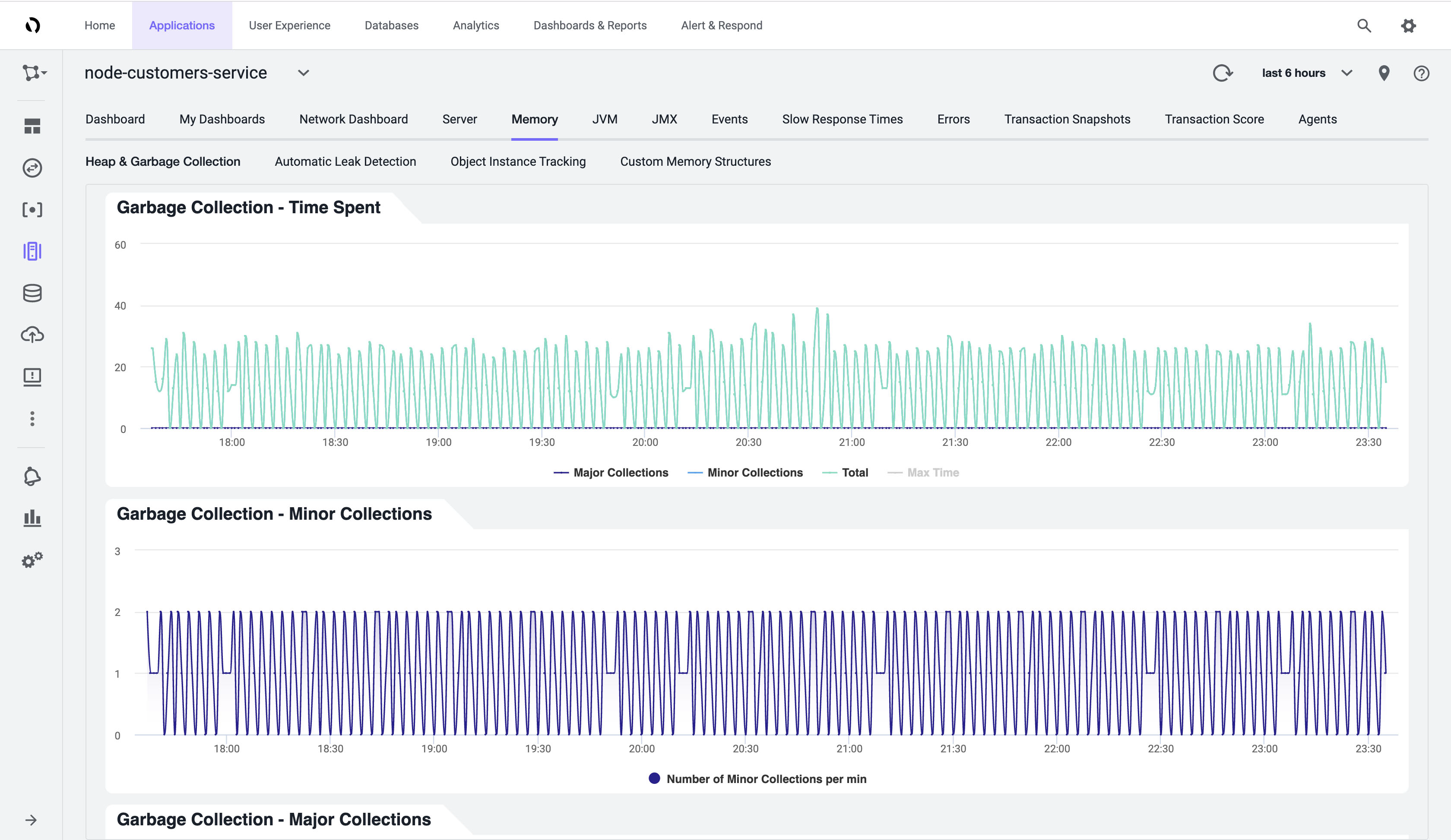
Prerequisites
To monitor the Spring Cloud workloads with AppDynamics, you can use the agent with your Azure Spring Cloud application. To do this, perform these steps:
- Create an Splunk AppDynamics account
- Install the Azure CLI. For instructions, see How to install the Azure CLI.
Limitations
The Java Agent is deployed as a read-only artifact within the Azure Spring Cloud environment. This results in some limitations in features available through the Java agent. The limitations are:
- Agent configuration through files (
controller-info.xml,agent. properties) is not available. - Configuration of agent logging levels through files (
log4j2.xml) is not available. - Custom correlation configuration through XML file is not available.
Use the Java Agent with Azure Spring Cloud
You can activate the Java Agent with the Azure Spring Cloud apps in these two ways:
- Activate the AppDynamics Java in-process Agent with Azure CLI
- Activate the AppDynamics Java in-process Agent with Azure Portal
Activate the Splunk AppDynamics Java in-process Agent with Azure CLI
- Create an instance of Azure Spring Cloud.
Create an application:
```shell az spring-cloud app create --name "appName" --is-public true \ -s "resourceName" -g "resourceGroupName"```CODE- Create a deployment with the Splunk AppDynamics agent and environment variables.
You must access the APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_ACCOUNT_ACCESS_KEY, APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_ACCOUNT_NAME and APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_HOST_NAME to connect to AppDynamics and customize other variables as per your requirement.
```shell
az spring-cloud app deploy --name "appName" --jar-path app.jar \
-s "resourceName" -g "resourceGroupName" \
--jvm-options="-javaagent:/opt/agents/appdynamics/java/javaagent.jar" \
--env APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_APPLICATION_NAME=<YOUR_APPLICATION_NAME> \
APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_ACCOUNT_ACCESS_KEY=<YOUR_AGENT_ACCESS_KEY> \
APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_ACCOUNT_NAME=<YOUR_AGENT_ACCOUNT_NAME> \
APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_NODE_NAME=<YOUR_AGENT_NODE_NAME> \
APPDYNAMICS_AGENT_TIER_NAME=<YOUR_AGENT_TIER_NAME> \
APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_HOST_NAME=<YOUR_APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_HOST_NAME> \
APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_SSL_ENABLED=true \
APPDYNAMICS_CONTROLLER_PORT=443Azure Spring Cloud pre-installs the Java Agent to the following path: /opt/agents/appdynamics/agent/javaagent.jar.
Activate the Splunk AppDynamics Java in-process Agent with Azure Portal
- On the Azure portal, find the app you want to monitor by clicking Settings > Apps on the left navigation pane.
- Click the application to navigate to the Configuration page.
- Click Configuration on the left navigation pane to add, update, or, delete the environment variables of the application in the Environment variables tab.
Click General settings to add, update or delete the JVM Options of the application in the General settings tab.
Click Save.
Click Restart to ensure the configuration is complete.
Configure Using the Environment Variables or System Properties
You can use these environment variables to configure the setup to use the agent with your Azure Spring Cloud application:
| Environment Variable |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
You can also use these system properties:
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
For a description of these system properties, see Java Agent Configuration Properties. To locate the account and account access key, see Agent-to-Controller Connections.
Splunk AppDynamics Agent Logging
By default, Azure Spring Cloud prints the info level logs of the Splunk AppDynamics agent to STDOUT. The logs are mixed with the application logs. You can find the explicit agent version from the application logs.
You cannot configure the controller-info.xml. Therefore, to obtain debug logs, you must set the environment variable for the log level on the app within ASC and then restart the app.
To run the command for capturing the ASC logs, see az spring-cloud app log.